
Projectile motion refers to the motion of an object that is thrown or projected into the air and is subject to the force of gravity. The key characteristic of projectile motion is that the object follows a curved path, known as a trajectory, rather than a straight line. This type of motion is a result of the combination of horizontal motion (in the direction of the initial velocity) and vertical motion (affected by gravity).
Here are some key concepts and characteristics of projectile motion:
- Launch Angle: The angle at which the projectile is launched with respect to the horizontal is known as the launch angle. The trajectory and range of the projectile depend on this angle.
- Initial Velocity: The speed and direction with which the projectile is launched are represented by the initial velocity. It can be broken down into horizontal and vertical components.
- Horizontal Motion: The horizontal motion of the projectile is typically uniform and unaffected by air resistance (assuming no air resistance). The horizontal velocity remains constant throughout the motion.
- Vertical Motion: The vertical motion is influenced by gravity. The vertical velocity changes over time due to the acceleration caused by gravity (9.8 m/s² on the surface of the Earth). The vertical motion can be described using the equations of motion.
- Trajectory Shape: The combination of horizontal and vertical motion results in a curved trajectory, which is typically a parabola. The shape of the trajectory is determined by the launch angle and initial velocity.
- Range: The range of a projectile is the horizontal distance it travels before hitting the ground again. The range depends on the initial velocity and launch angle.
- Maximum Height: The maximum height reached by the projectile is another important parameter. It depends on the launch angle and initial velocity.
Key equations for projectile motion (assuming constant gravitational acceleration and neglecting air resistance):
Here,
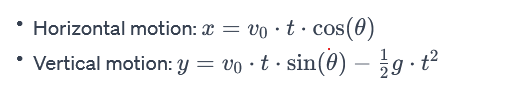
- x and y are the horizontal and vertical positions,
- v0 is the initial velocity,
- θ is the launch angle,
- g is the acceleration due to gravity, and
- t is the time of flight.
Projectile motion is a common topic in physics and is used to analyze the motion of objects like projectiles, such as thrown balls, launched rockets, or even celestial bodies in motion.
