Velocity is the rate at which an object changes its position in a specific direction. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude (speed) and direction. Velocity tells not just how fast something is moving (speed), but also in which direction it is moving.
Formula for Velocity:
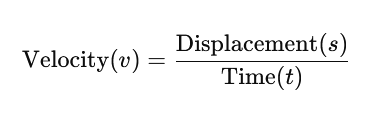
- Displacement refers to the straight-line distance from the starting point to the final point, considering direction.
- Time is the duration over which the displacement occurs.
Key Points:
- Vector Quantity: It includes both magnitude and direction.
- SI Unit: The standard unit of velocity is meters per second (m/s).
- Uniform Velocity: When an object covers equal displacements in equal time intervals in the same direction.
- Changing Velocity: If either the speed or direction (or both) change, the velocity is considered non-uniform.
Example:
- Scenario 1: If a car moves 100 meters east in 10 seconds, its velocity can be calculated as:
- Scenario 2: If the same car moves 50 meters north in 5 seconds, its velocity will be:
Thus, velocity gives not only the speed (10 m/s) but also the direction (east or north in these examples).
Difference from Speed:
While speed measures how fast an object is moving, velocity also includes the direction of motion. For example, if a car moves at 60 km/h in a circle, its speed is constant, but its velocity is changing because its direction is continuously changing.
